Symptoms
While most HPV do not show any symptoms, some strains of HPV infection can lead to the development of warts on the body. Different types of HPV can lead to warts on different parts of the body, as well as in the genital region and in the mouth, usually from sexual contact.
Warts that are associated with HPV include:
- Common warts (verruca vulgaris)
- Filiform warts
- Flat plane warts (verruca plana)
- Plantar warts (verruca plantaris/ verruca palmaris)
- Periungual warts
- Butchers warts
More details about warts can be found here.
Non-genital warts
Warts may appear as fleshy skin-colored bumps (papules), scaly rough and hard (common warts), or thin and sticking out, with “church spire” peaks (filiform warts). Flat warts in particular may be difficult to see as they are skin coloured and quite flat to the skin; these can sometimes be itchy and lead to further spread of the virus from scratching. On the hands and feet, they may be thicker, and may sometimes be painful (palmoplantar/myrmecia). If these are grouped together, they can be called mosaic warts. Some areas can be more difficult to treat, like warts around the nails, known as periungual warts. Butcher’s warts are commonly seen in butchers or other people who handle meat.
 |
 |
 |
||
|
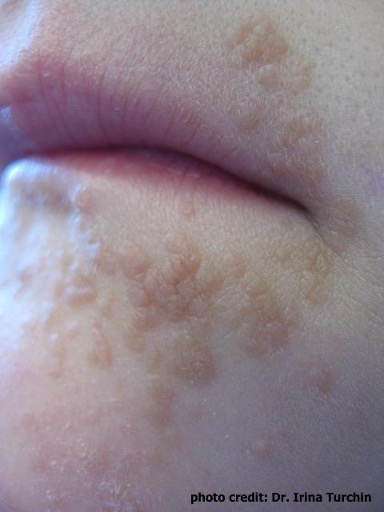
Image 2: HPV flat warts (verucca plana) around the mouth and lips area.(Photo courtesy of Dr. Irina Turchin)
|
|
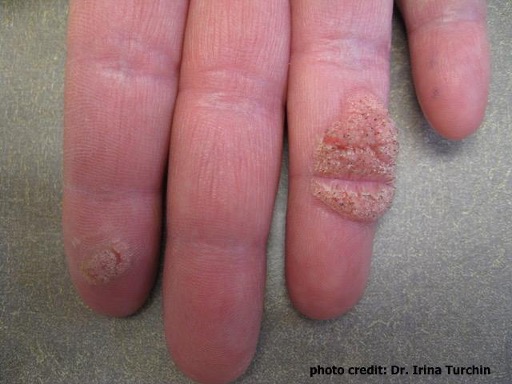
Image 3: Plantar warts (verruca palmaris) on the palm of the hand. (Photo courtesy of Dr. Irina Turchin)
|
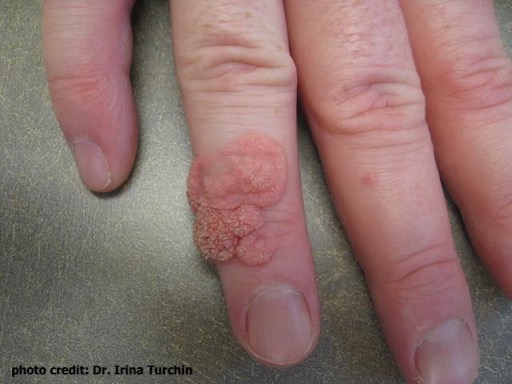
Image 4: Common wart (verruca vulgaris) on the back of the hand/finger. (Photo courtesy of Dr. Irina Turchin)
|
|
 |
 |
|||
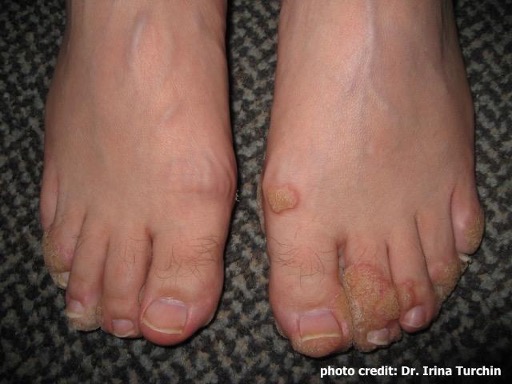
| Image 5: Periungual warts around the nails of the toes. (Photo courtesy of Dr. Irina Turchin) |
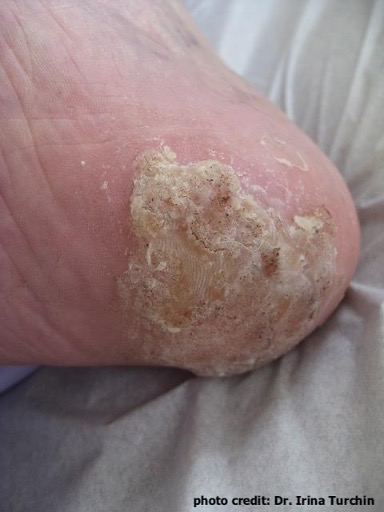
Image 6: Plantar wart (verruca plantaris) seen as a verrucous plaque on the heel of the foot. (Photo courtesy of Dr. Irina Turchin) |
Genital warts
Genital warts are caused by certain strains of HPV and arise around the genitals and the anus, together they are sometimes known as anogenital warts. The size and number of warts may vary, and the color of the warts can range anywhere from a fleshy brown to a dull pink. Management of the warts depends on the size, appearance, location and number of warts present. More information on genital warts can also be found in our section on ‘Warts’.