The information in this section has been gathered from existing peer-reviewed and other literature and has been reviewed by expert dermatologists on the CSPA Medical Advisory Board.
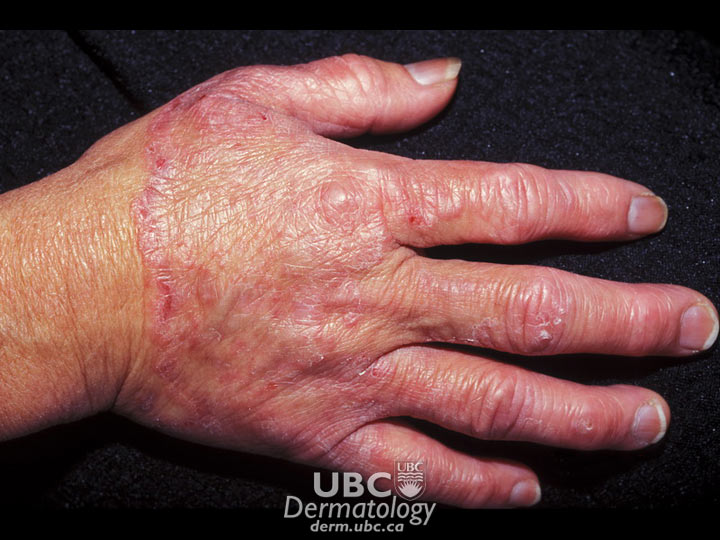
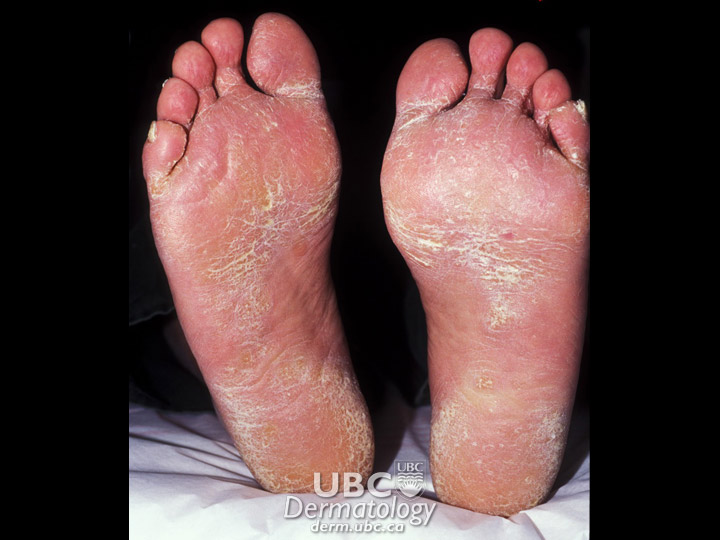
Fungal infections are infections caused by fungi, organisms related to moulds, mushrooms and mildew. They live in the air, water and soil, and on plants. About half of all fungi are harmful to humans. Fungal infections are rarely life-threatening, but they can be contagious and can lead to a number of skin conditions, including:
- Athlete's foot
- Jock itch
- Ringworm
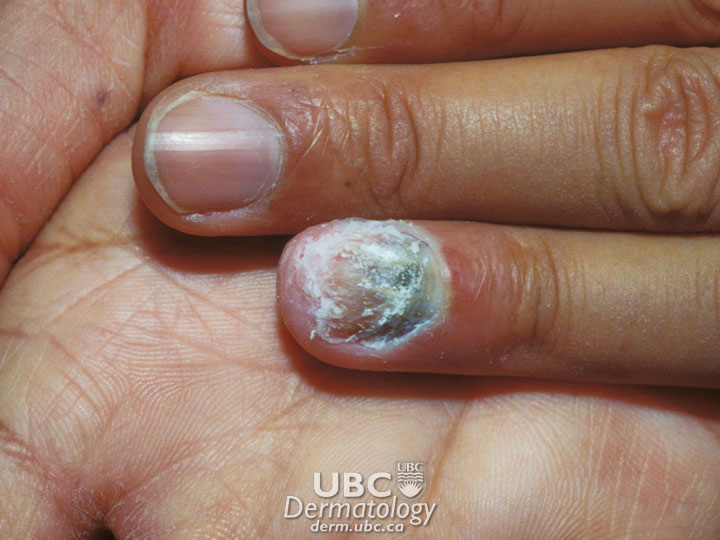
- Nail infections
- Scalp infections
- Candidiasis (thrush)
- Oral intertrigo
- Vulvovaginitis
- Diaper rash
- Paronchia
- Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis
Each fungus has adapted in a particular way to thrive in specific parts of the body. For example, the fungus associated with nail infections lives on the keratin (protein) in the nail, whereas the fungus that causes athlete's foot lives on the dead skin between the toes.
Risk factors for fungal infections include:
- Poor blood circulation (e.g., in persons with diabetes)
- High skin moisture content due to sweating, insufficient towelling off after a bath or shower, wearing tightly fitting or airtight clothing, walking barefoot in wet environments such as gyms, shower rooms or around swimming pools
- Excessive or deficient physical hygiene
- Damaged skin from wearing tightly fitting shoes